RO (Reverse Osmosis) water is known for its purity and effectiveness in removing contaminants like bacteria, heavy metals, and chemicals. This thorough filtration process provides clean, safe drinking water, making it a popular choice for households.
However, there are common questions about its mineral content, acidity, and overall impact on health. Here’s everything you need to know about RO water, including its benefits, concerns, and practical solutions.
Table of Contents
- What is RO Water?
- Does RO Systems Remove Minerals from Water?
- Is RO Water the Same as Distilled?
- What is the pH of RO Water?
- Why Is My RO Water Cloudy?
- Is RO Water Safe to Drink Long Term?
What is RO Water?
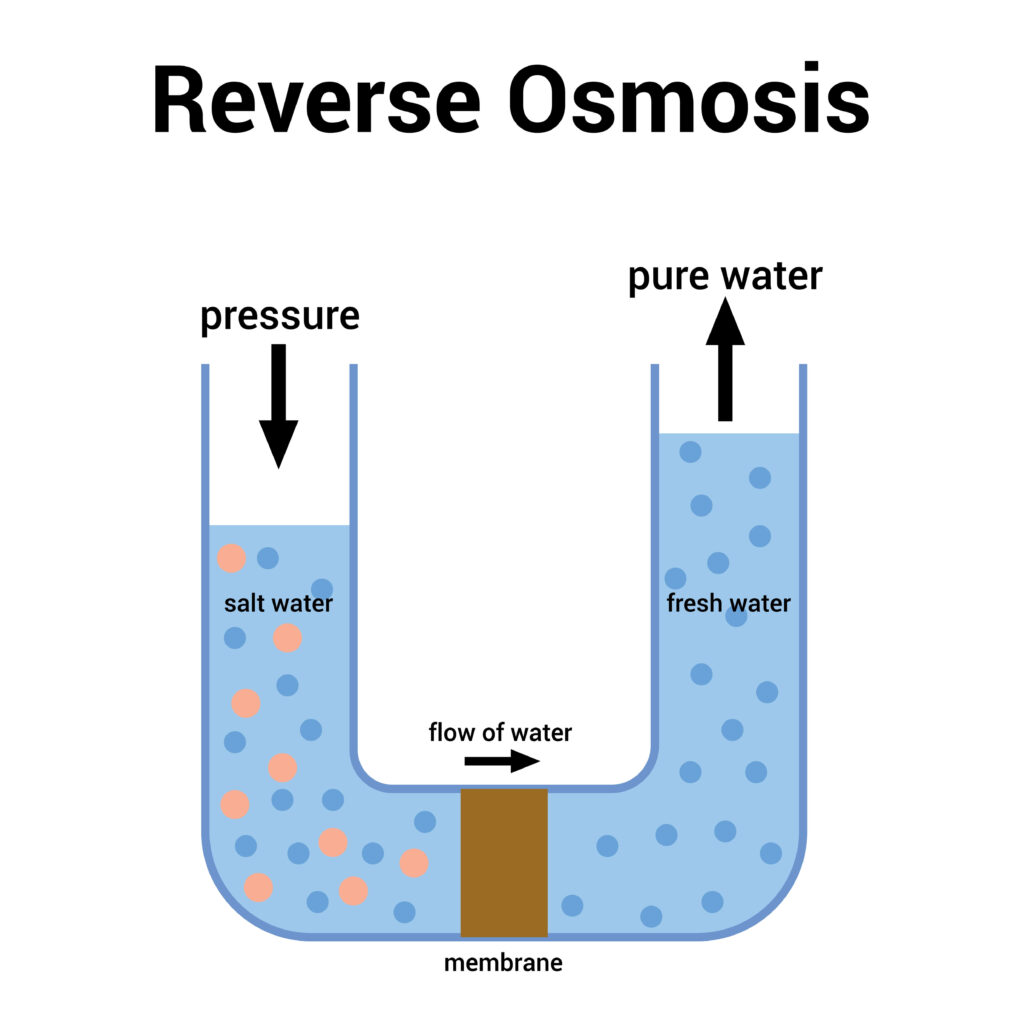
Reverse osmosis (RO) water has undergone reverse osmosis filtration to remove contaminants, making it much purer than untreated water. RO water filtration is a popular method for improving water quality in homes, businesses, and industrial settings. The reverse osmosis process uses a semi-permeable membrane to filter out impurities, including dissolved salts, chemicals, and bacteria, leaving behind clean and refreshing water.
How Does it Work?
Reverse osmosis (RO) forces water through a semipermeable membrane, blocking contaminants like salts, minerals, and bacteria. The impurities are flushed away, leaving purified water.
RO systems use several filtration stages: a pre-filter removes large particles, the membrane filters out contaminants, and a post-filter refines the water. This process removes substances like lead, arsenic, and some viruses, making the water ideal for drinking and household use.

Does RO Soften Water?
RO systems don’t soften water in the same way as water softeners, which replace calcium and magnesium with sodium to prevent scale buildup. While RO removes most calcium and magnesium, it doesn’t add sodium or alter the water’s chemistry. It reduces hardness but isn’t a true softening process.
For very hard water, combining a water softener with an RO system is effective: the softener handles hardness, and the RO system purifies the water.
Does RO Systems Remove Minerals from Water?
Many people turn to reverse osmosis (RO) systems for clean and safe drinking water. These systems are renowned for removing a wide range of contaminants, but do they also strip water of its beneficial minerals?
Understanding Reverse Osmosis Systems
Reverse osmosis systems purify water by pushing it through a semi-permeable membrane that removes contaminants like bacteria, viruses, heavy metals, and chemicals, resulting in clean, safe drinking water.

A common concern is that RO systems also remove essential minerals like calcium and magnesium. While they do lower mineral levels, understanding the impact and available solutions is important.
How to Restore Minerals in RO Water
- Mineral Drops: Add mineral drops to your RO water to replenish lost essential minerals. Follow the product instructions for proper use.
- Remineralization Filters: Install a remineralization filter in your RO system to easily restore minerals. These filters integrate seamlessly into most systems.
- Diet and Nutrition: A balanced diet with fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds provides essential minerals, reducing reliance on supplements.
What Does RO Water Remove?
To fully appreciate the benefits of RO systems, it’s helpful to know exactly what contaminants they remove from water:
- Chemical Contaminants: RO systems effectively remove chemical contaminants such as chlorine, fluoride, and pesticides. These chemicals can harm health, making their removal crucial for safe drinking water.
- Heavy Metals: Due to industrial pollution, heavy metals like lead, mercury, and arsenic can be present in water supplies. RO systems can filter out these toxic substances, ensuring your water is safe to drink.
- Biological Contaminants: Pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, and protozoa can cause serious illnesses if consumed. RO systems effectively eliminate these biological contaminants, providing additional safety for drinking water.
Is RO Water the Same as Distilled?
Two methods often come up in the quest for pure, clean water: Reverse Osmosis (RO) and Distillation. Both promise to deliver high-quality water, but are they the same? Understanding the nuances is key to making an informed choice, whether for your home, boat, or any other application.
Can You Drink RO Water
Yes, you can drink RO water, which is safe and clean for consumption. The Reverse Osmosis (RO) filtration process effectively removes contaminants such as dissolved salts, bacteria, and other impurities, resulting in highly purified water.
However, because RO also eliminates beneficial minerals like calcium and magnesium, the water can taste flat. For people who rely on water as a mineral source, this may not be ideal. To address this, many systems add minerals back into the water after filtration. Overall, RO water is an excellent choice for those who want a higher level of purity.

What is RO Water?
Reverse Osmosis (RO) is a water purification process that uses a semi-permeable membrane to remove ions, molecules, and larger particles from drinking water. Water is forced through the membrane during this process, leaving contaminants behind.
Safety and Benefits
RO water is generally safe to drink and offers several benefits:
- Removes Contaminants: RO systems can effectively remove contaminants, including bacteria, viruses, heavy metals, and even certain chemicals.
- Improves Taste: By removing impurities, RO water often tastes better than tap water.
- Versatility: RO systems can be used in homes, boats, and industrial applications.
Considerations
However, there are a few considerations to keep in mind:
- Mineral Removal: RO also removes essential minerals like calcium and magnesium. While this isn’t a deal-breaker, it’s something to consider.
- Waste Water: The RO process produces some wastewater, which may concern eco-conscious individuals.
RO Water vs. Distilled
The Distillation Process
Distillation involves boiling water to produce steam, which is then condensed into liquid form. This process leaves most contaminants behind but takes longer and requires more energy.
Key Differences
Purity Levels
- RO Water: Removes up to 99% of contaminants but may leave behind some dissolved gases.
- Distilled Water: Nearly 100% pure, as the boiling process eliminates almost all impurities.
Taste and Use
- RO Water: Often has a fresher taste and is suitable for daily drinking and cooking.
- Distilled Water: Tends to have a flat taste due to lacking minerals. It’s ideal for medical applications and household appliances like irons and humidifiers.
Cost and Efficiency
- RO Systems: Generally more economical to operate over time, especially with systems like those offered by Cruise RO Water and Power, which are designed for efficiency.
- Distillation: More energy-intensive and slower, making it less practical for high-volume needs.
What is the pH of RO Water?
Reverse osmosis (RO) water is a popular choice for those seeking purified and contaminant-free drinking water. RO systems effectively remove impurities, chemicals, and dissolved solids, providing high-quality water for everyday consumption.
However, a common question among consumers is: What is the pH of RO water? Understanding the pH level of RO water is essential because it affects not only the taste but also its compatibility with different diets and health recommendations.

Is RO Water Acidic?
Yes, RO water is slightly acidic. This happens because the reverse osmosis process removes minerals like calcium and magnesium that buffer pH, leaving highly pure water. Without these minerals, RO water usually has a pH of 5.0 to 7.0. It can also absorb carbon dioxide from the air, forming carbonic acid. While this slight acidity isn’t harmful for drinking, it may affect certain uses, like in aquariums or hydroponics.
Is RO Water Alkaline?
RO water is not naturally alkaline; it’s typically slightly acidic. To make it alkaline, some people add minerals like calcium or magnesium, a process called remineralization. This raises the pH to neutral or slightly alkaline.
Supporters of alkaline water claim it offers benefits like better hydration and increased energy, though research is ongoing. Adding a remineralization filter to an RO system is common for achieving a more balanced pH.
Why Is My RO Water Cloudy?
Reverse osmosis (RO) water filtration systems are known for producing high-quality, purified water. However, if you’ve noticed that your RO water is cloudy, you might wonder if something’s wrong with your system. Cloudy RO water can be unsettling, but the issue is typically harmless and easy to address.
Does RO Water Dehydrate You?
A common misconception about reverse osmosis (RO) water is that it can cause dehydration because the RO process removes almost all impurities, including beneficial minerals like calcium and magnesium. However, this belief is incorrect.
RO water hydrates the body just as effectively as regular water. Hydration depends on water itself, not the minerals it may contain. The lack of minerals in RO water doesn’t affect its ability to hydrate. These minerals are easily obtained from a balanced diet or supplements, so there’s no risk of dehydration from drinking RO water.
In fact, RO water may be healthier since it’s free of contaminants like chlorine, lead, and arsenic, often found in unfiltered tap water. While it’s not the same as an electrolyte-rich drink, RO water remains a clean and safe hydration choice.
Does RO Water Hydrate You?
Yes, RO water provides effective hydration. The main purpose of drinking water is to maintain your body’s fluid levels, and RO water does this while being free from harmful contaminants. Although the filtration process removes minerals, it doesn’t impact the water’s ability to hydrate.
Hydration depends on the quantity of water you drink, not the minerals in it. To replenish lost electrolytes after exercise or illness, you may prefer mineral water or an electrolyte drink. RO water works perfectly well for everyday hydration. If you’re concerned about missing minerals like calcium or magnesium, you can add mineral drops to your RO water.
Cloudiness in RO water is usually due to trapped air bubbles, especially after a new installation or when the storage tank is freshly filled. This is harmless and should clear up within minutes as the bubbles dissipate.
Is RO Water Safe to Drink Long Term?
Health enthusiasts and professionals have debated reverse osmosis (RO) water. While it’s praised for its purity, there are questions about its long-term safety.
Is RO Water Bad for Kidneys?

Understanding RO Water
Reverse osmosis is a filtration process that removes contaminants from water by using pressure to force water molecules through a semipermeable membrane. This process effectively strips away impurities, leaving you with spotless water. However, it removes essential minerals like magnesium, calcium, and potassium.
The Role of Minerals in Kidney Health
Your kidneys play a crucial role in maintaining your body’s mineral balance. Minerals like calcium and magnesium are vital for various bodily functions, including muscle function and bone health. The absence of these minerals in RO water may lead to deficiencies if not supplemented through diet or other means.
Scientific Perspective
While limited research directly links RO water to kidney problems, some studies suggest that drinking demineralized water over long periods may not be ideal. A lack of essential minerals can lead to imbalances that could affect kidney function. However, to mitigate any risks, it’s vital to consider other dietary sources of these minerals.
Can Bacteria Grow in RO Water?
The Purity of RO Water
One of the primary benefits of RO water is its high purity level. The filtration process removes bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens, making drinking safer than untreated water. However, once stored, RO water is not immune to bacterial growth.
Storage Concerns
Bacteria can grow in RO water if it’s stored improperly. For instance, even RO water can become contaminated in a poorly sanitized container or an environment conducive to bacterial growth. To prevent bacterial contamination, it’s crucial to store RO water in clean, airtight containers and consume it within a reasonable timeframe.
Prevention Methods
To ensure the long-term safety of RO water, consider adding UV sterilizers or other disinfection methods to your water storage system. These additional steps can help maintain the purity of your RO water and prevent bacterial growth.
Quality RO systems with Cruise RO
RO water delivers exceptional purity by removing harmful contaminants, making it a safe and reliable choice for hydration. While concerns about mineral loss and acidity can be addressed through simple solutions like remineralization or a balanced diet, RO water offers substantial health benefits.
Ready to experience cleaner, safer water? Explore high-quality RO systems today and take a step toward better hydration and well-being only with Cruise RO Water & Power! Contact us!




